When facing knee osteoarthritis, choosing between a Total Knee Replacement (TKR) and a Minimally Invasive Partial Knee Replacement (PKR) depends on several factors, including the extent of the joint damage, patient lifestyle, and medical history.
Understanding the difference
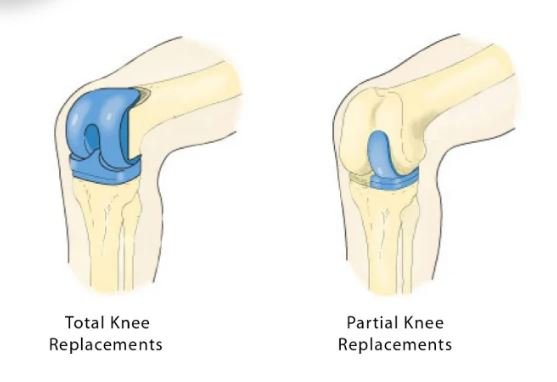
Total Knee Replacement (TKR) Also known as knee arthroplasty, this procedure involves replacing the entire knee joint with an artificial one. It is designed to alleviate pain and restore mobility by removing all the damaged cartilage and replacing it with metal and plastic implants.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR) is a minimally invasive surgery that targets only the most damaged areas of cartilage. It preserves healthy parts of the knee, leading to a quicker recovery and smaller incisions compared to TKR.
Scopes and Recovery:
Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
- Scope: TKR involves replacing the entire knee joint, suitable for patients with widespread arthritis.
- Recovery: While effective, TKR has a longer recovery time and involves more post-surgical rehabilitation.
Minimally-Invasive Partial Knee Replacement (PKR):
- Scope: PKR is designed for patients with arthritis and is limited to one compartment of the knee. Only the damaged portion is replaced, preserving healthy bone and tissue.
- Recovery: The minimally invasive approach leads to a faster recovery, less pain, and smaller incisions. Patients often return to daily activities sooner than those undergoing TKR.
Factors to Consider:
- Extent of Arthritis: If arthritis affects the entire knee, TKR is the better option. PKR can be sufficient for localized damage.
- Age and Activity Level: Younger, more active patients might benefit from PKR, as it retains more of the knee’s natural structure, allowing for greater mobility post-surgery.
- Recovery Goals: Patients seeking a quicker recovery and return to daily activities might prefer PKR. However, TKR might offer a more comprehensive long-term solution for severe cases.
Conclusion:
Deciding between TKR and PKR requires a thorough evaluation by an orthopedic surgeon. Understanding the pros and cons of each procedure helps patients make informed decisions aligned with their health goals. Consulting with a surgeon about personal health history, lifestyle, and the extent of knee damage will lead to the best outcome.