Introduction
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a revolutionary surgical procedure designed to relieve chronic knee pain and restore function. It is generally recommended for patients with knee joint damage from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis. By replacing the damaged knee surface with a prosthetic component, TKR helps patients regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
Indications for Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
TKR may be recommended for individuals whose:
- Knee pain and stiffness are still severe.
- Limited mobility which affects daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs
- Orthodox treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, and injections, do not provide relief from symptoms.
Procedure Overview: Total knee replacement surgery involves the following important steps:
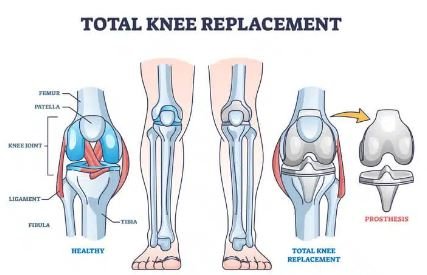
- Anesthesia: The patient will receive general or regional anesthesia.
- Tap: A precise cut is made above the knee to access the joint.
- Bone regeneration: Damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the femur. (thigh bone) shin bone (shin bone) and possibly the patella (knee bone).
- Implant placement: The prosthetic components are positioned to recreate the natural function of the knee joint.
- Closure: The incision is closed, and the knee is generally placed in a brace or cast for protection during recovery.
Types of Implants in TKR:
The type of implants used in TKR depends on factors such as the patient’s anatomy, age, and activity. The following are the main types of knee implants:
1) Fixed bearing implants:
- Description: Most commonly used type. It has a fixed bearing surface attached to the tibial component.
- Advantages: Provides excellent stability and is suitable for most patients.
- Thoughts: It can wear out over time. This is especially true of younger, more active people.
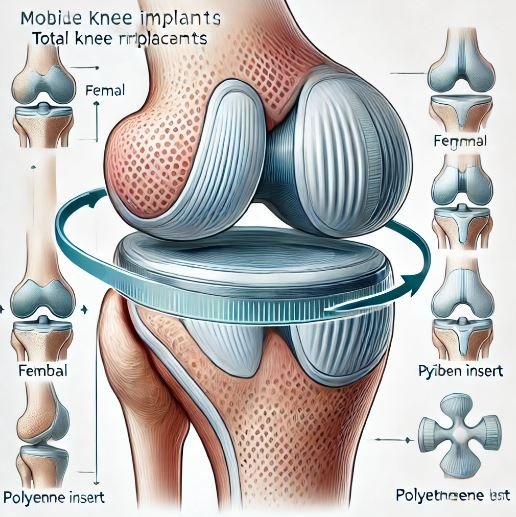
2) Mobile-Bearing Implants:
- Description: Features polyethylene inserts for more natural movement.
- Advantages: Designed to reduce wear on bearing surfaces. This may increase the life of the implant.
- Considerations: Careful surgical technique is required and there may be a high risk of distraction.
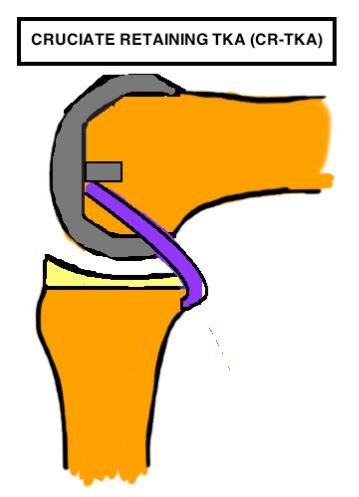
3) Cruciate-Retaining Implants:
- Description: Preserves the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), enhancing the natural stability of the knee joint.
- Benefits: PCL placement can improve knee self-sensing and function.
- Considerations: Not suitable for patients with severe PCL injuries.
4) Cruciate-Substituting Implants:
- Description: Designed for cases where the PCL is damaged or missing.
- Benefits: Helps patients with osteoarthritis of the knee-tendon to have more stability.
- Considerations: Slight differences may be felt during movement due to changes in knee mechanics.
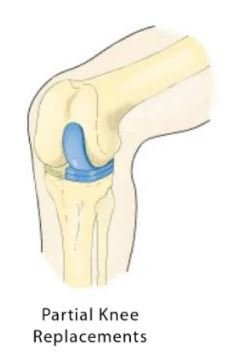
5) Partial knee implants:
- Description: Replace only the damaged part of the knee. By leaving healthy bone tissue intact.
- The benefit is that it is minimally invasive. recover faster and the function of the knee joint is more natural
- Attention: Suitable only for patients with arthritis or local injury.
6) Custom implants:
- Description: Designed to fit the patient’s specific anatomy using 3D imaging and printing technology.
- Advantages: Provides precise alignment and improved results.
- Considerations: Detailed pre-surgery planning is required and is usually more expensive.
Conclusion Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is a solution for people suffering from severe knee osteoarthritis. Selecting the right implant that combines advanced surgical techniques with state-of-the-art implant technology can help patients regain mobility. reduce pain and improve overall well-being is important, Dr.Vivek Logani should do so after a thorough evaluation with an experienced orthopedic surgeon such as Dr. Vivek Logani.

Whether you are considering TKR for the first time or considering various implant options, Dr. Vivek Logani’s expertise ensures that your surgery will be customized to meet your unique needs. Helps you return to an active lifestyle again.
1 Comment
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This website features buggy hire on the island of Crete.
You can safely arrange a buggy for exploration.
Whether you’re looking to explore hidden beaches, a buggy is the exciting way to do it.
https://unsplash.com/@buggycrete
All vehicles are well-maintained and can be rented for full-day bookings.
Through our service is fast and comes with no hidden fees.
Begin the adventure and enjoy Crete like never before.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This online pharmacy features an extensive variety of pharmaceuticals with competitive pricing.
You can find both prescription and over-the-counter medicines suitable for different health conditions.
We strive to maintain high-quality products without breaking the bank.
Quick and dependable delivery provides that your purchase gets to you quickly.
Enjoy the ease of shopping online through our service.
priligy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
It’s alarming to realize that over 60% of medication users make dangerous medication errors stemming from insufficient information?
Your wellbeing is your most valuable asset. Each pharmaceutical choice you implement significantly affects your long-term wellbeing. Staying educated about medical treatments should be mandatory for successful recovery.
Your health depends on more than taking pills. Each drug interacts with your physiology in specific ways.
Remember these essential facts:
1. Mixing certain drugs can cause dangerous side effects
2. Even common pain relievers have potent side effects
3. Skipping doses undermines therapy
To protect yourself, always:
✓ Check compatibility with professional help
✓ Review guidelines in detail when starting any medication
✓ Ask your pharmacist about potential side effects
___________________________________
For professional drug information, visit:
https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17910890
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы осуществляет помощью иностранных граждан в северной столице.
Мы помогаем в получении необходимых бумаг, прописки, а также формальностях, связанных с трудоустройством.
Наши специалисты помогают по вопросам законодательства и дают советы правильный порядок действий.
Оказываем поддержку по вопросам временного проживания, и в вопросах натурализации.
С нами, процесс адаптации станет проще, упростить оформление документов и комфортно устроиться в этом прекрасном городе.
Пишите нам, для консультации и помощи!
https://spb-migrant.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Even with the rise of modern wearable tech, traditional timepieces continue to be everlasting.
A lot of enthusiasts value the craftsmanship that defines classic automatics.
In contrast to modern wearables, that need frequent upgrades, classic timepieces stay relevant over time.
http://couroberon.com/Salons/viewtopic.php?t=517
Luxury brands still produce exclusive mechanical models, showing that demand for them is as high as ever.
To a lot of people, a mechanical watch is not just an accessory, but a reflection of craftsmanship.
Though digital watches offer convenience, traditional timepieces carry history that remains unmatched.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Центр ментального здоровья — это пространство, где помогают о вашем психике.
Здесь работают профессионалы, стремящиеся помочь в трудные времена .
Цель центра — укрепить эмоциональное равновесие клиентов.
Услуги включают терапию для решения проблем и трудностей.
Такой центр создает комфортную атмосферу для развития.
Обращение сюда — шаг к гармонии и внутреннему покою.
https://www.comforttime.net/2023/06/22/the-power-of-effective-communication-in-business
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Центр ментального здоровья — это место, где каждый может получить помощь и профессиональную консультацию.
Специалисты работают с различными проблемами, включая повышенную тревожность, эмоциональное выгорание и психологический дискомфорт.
http://www.5star-auto.com
В центре применяются современные методы лечения, направленные на восстановление внутренней гармонии.
Здесь создана комфортная атмосфера для открытого общения. Цель центра — поддержать каждого обратившегося на пути к психологическому здоровью.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На данном сайте вы найдете полезные сведения о психическом здоровье и способах улучшения.
Мы рассказываем о методах развития эмоционального равновесия и борьбы со стрессом.
Экспертные материалы и советы экспертов помогут разобраться, как поддерживать психологическую стабильность.
Важные темы раскрыты доступным языком, чтобы любой мог найти нужную информацию.
Начните заботиться о своем ментальном состоянии уже прямо сейчас!
healthyvisitors.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша компания помогает увеличить просмотры и аудиторию во ВКонтакте. Мы предлагаем эффективное продвижение, которое способствует увеличению активности вашей страницы или группы. ВК просмотры бесплатно накрутка онлайн бесплатные Аудитория активные, а просмотры добавляются быстро. Гибкие тарифы позволяют подобрать оптимальный вариант для разного бюджета. Оформление услуги максимально прост, а результат не заставит себя ждать. Начните продвижение сегодня и сделайте свой профиль заметнее!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На данном сайте вы можете заказать аудиторию и реакции для Telegram. Мы предлагаем активные аккаунты, которые способствуют развитию вашего канала. Быстрая доставка и гарантированный результат обеспечат успешное продвижение. Цены доступные, а процесс заказа занимает минимум времени. Запустите продвижение уже сегодня и увеличьте активность в своем Telegram!
Накрутить подписчиков в Телеграмм канал бесплатно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На данном сайте вы можете приобрести подписчиков для Telegram. Мы предлагаем активные аккаунты, которые помогут развитию вашего канала. Быстрая доставка и стабильный прирост обеспечат надежный рост подписчиков. Тарифы доступные, а процесс заказа максимально прост. Запустите продвижение уже сейчас и нарастите аудиторию своего канала!
Накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм живые купить
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На нашем сайте вы можете купить подписчиков и лайки для TikTok. Мы предлагаем качественные аккаунты, которые помогут продвижению вашего профиля. Быстрая доставка и гарантированный результат обеспечат увеличение вашей активности. Цены доступные, а процесс заказа занимает минимум времени. Начните продвижение уже прямо сейчас и увеличьте охваты!
Накрутка просмотров Тик Ток
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На этом сайте АвиаЛавка (AviaLavka) вы можете купить дешевые авиабилеты в любые направления.
Мы предлагаем лучшие цены от надежных авиакомпаний.
Простой интерфейс позволит быстро найти подходящий рейс.
Airtickets
Интеллектуальный фильтр помогает подобрать оптимальные варианты перелетов.
Покупайте билеты онлайн без переплат.
АвиаЛавка — ваш удобный помощник в путешествиях!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здесь можно узнать способы диагностики и подходы по восстановлению.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
Особое внимание уделяется психологическим особенностям и их влиянию на эмоциональным состоянием.
Также рассматриваются эффективные медикаментозные и психологические методы поддержки.
Материалы помогут разобраться, как правильно подходить к угнетенным состоянием в пожилом возрасте.
Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this website on a regular basis, this website is genuinely pleasant and the viewers are really sharing nice thoughts.